An identity is something valid for ALL values of x. They can ALL be proved.
List of Identities (*) are important ones
- Transformation Identities
- Even and Odd Identities *
- Supplementary Function Identities *
- Co-Function Identities *
- Compound Angle Identity *
- Double Angle Identity *
- Reduction Identity
- Half Angle Identity *
- Sum to Product
- Product to Sum
Practical Identity Use
- Random Angle to Co-Function or Supp-Function Identity
- Equivalent Ratio Problem Solving Procedure ⇐ Good for understanding Co-Function
Proving Identities Techniques
General
- Separate LS and RS. You cannot cross terms between sides
- Try to change everything into terms of sin and cos
- Find common denominators
- Use Difference of Squares.
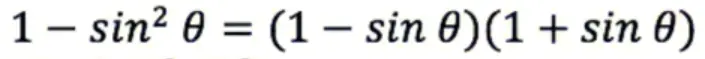
- Use power rule.
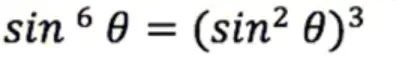
- Use more Transformation Identities during simplification
- Multiply by 1 if required
Specific
- If you see (1-cos),(1+cos),(1-sin),(1+sin) in the denominator, try multiplying the numerator and denominator by the conjugate. eg, conjugate of (1-cos) = (1+cos).
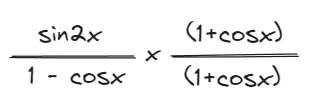
- If you see a fraction with 2 terms in numerator and 1 term in denominator, split that fraction in 2. parts
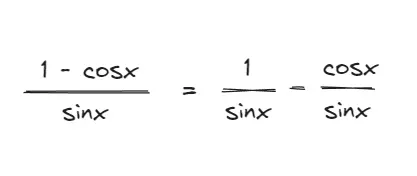
- If you see a fraction with 2 terms in numerator and 1 term in denominator, split that fraction in 2. parts