A Partitioning tool on modern windows systems.
Disk Initialization
All new drives must be initialized in the Disk Management software.
Right click your disk icon and select Initialize
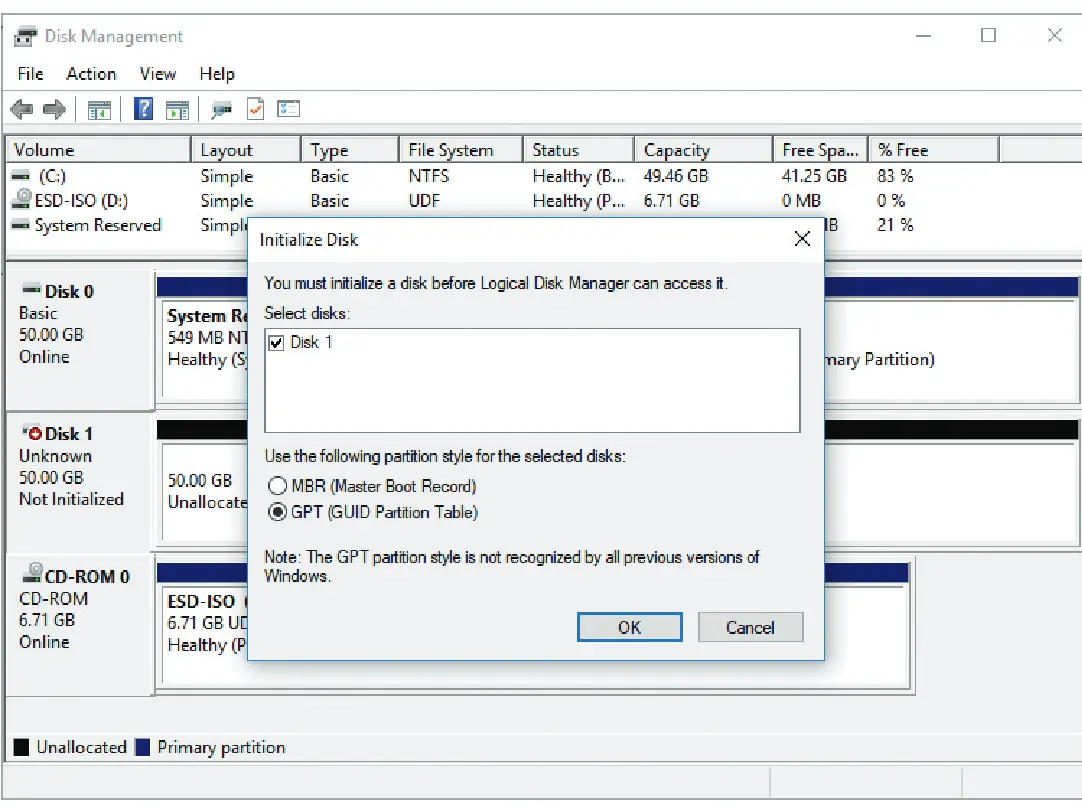 Once you give it the File System, you can see the status of the drive.
Once you give it the File System, you can see the status of the drive.
Drive Statuses
Healthy: Drive is usable as a file system Active: Drive is in use as a file system by the OS Unallocated: Drive is not partitioned Foreign Drive: A Windows Dynamic Disks drive from a foreign computer is used in this computer Formatting: A drive is currently being formatted Failed: Disk is damaged or corrupt
Creating Partitions/Volumes
Right click an unallocated drive, and then set the volume size
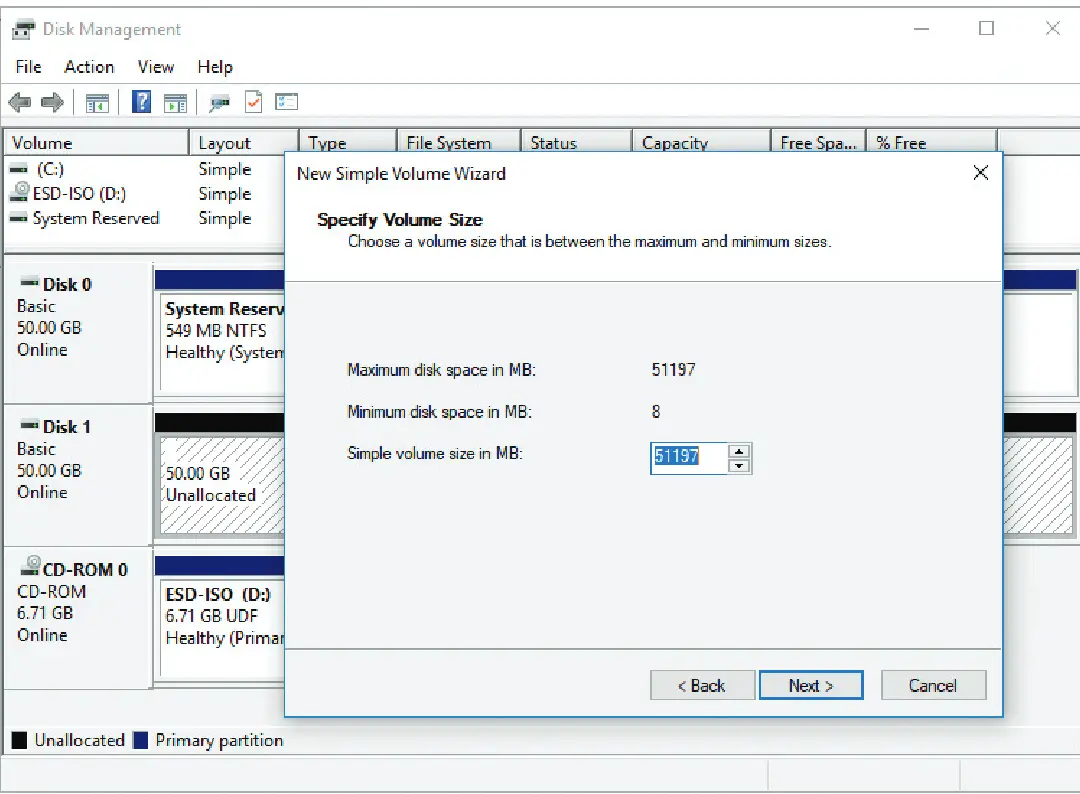 Then, you can format it with a File System.
You can choose the cluster size, whether to allow drive compression and formatting methods (Quick format or deep format)
Then, you can format it with a File System.
You can choose the cluster size, whether to allow drive compression and formatting methods (Quick format or deep format)
Dynamic Disks
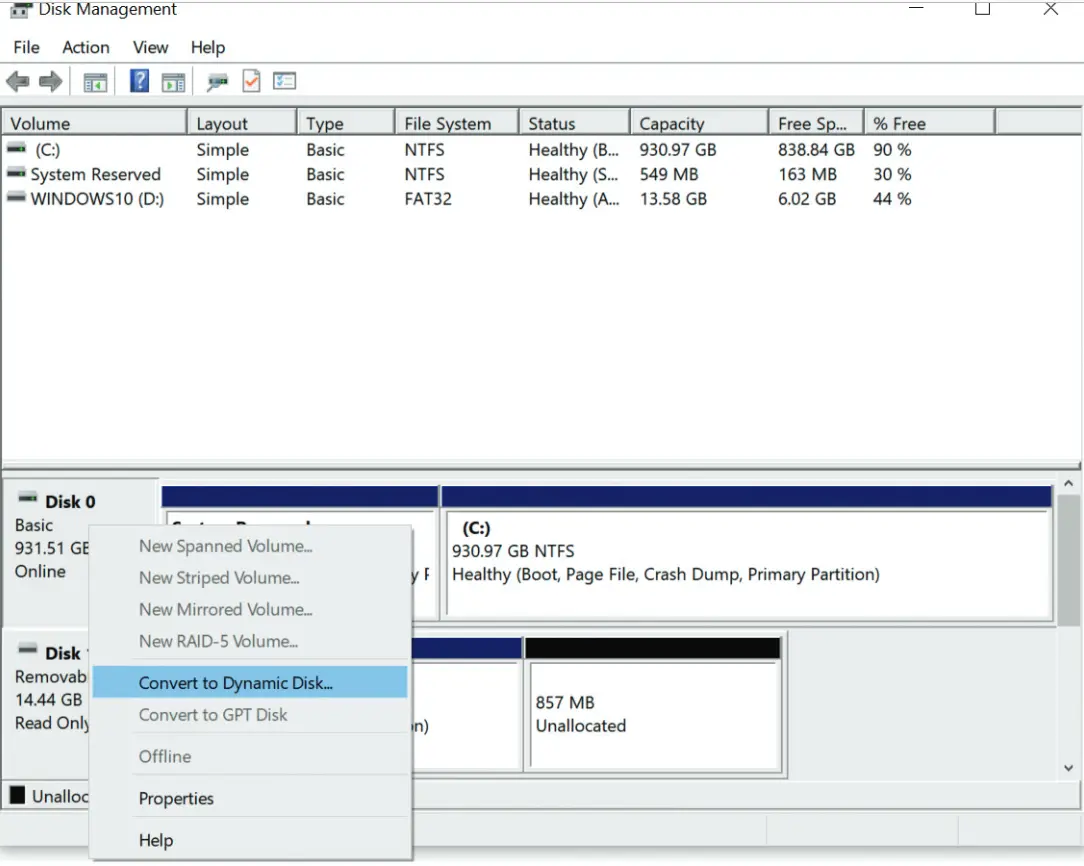 You can turn basic disks into Dynamic Disks. basic → dynamic is a clean process
dynamic → basic is a messy process that may lead to data loss/data corruption
You can turn basic disks into Dynamic Disks. basic → dynamic is a clean process
dynamic → basic is a messy process that may lead to data loss/data corruption
Partition/Volume Types
A dynamic disk will have the following parition types:
Simple Volumes
Functionally similar to a Primary Partition, except you cannot install an OS on it.
Spanning Volumes
A volume that utilizes space of several different disks. You can install a new drive on your system, and retain the same partition across several drives so essentially you have one file system comprised of several drives
Striped Volumes
If you have 2 or more dynamic drives, you can combine them into one striped volume. This is functionally similar to a RAID 0 array
Mirrored Volumes
Requires 2 or more dynamic drives. Mirror one drive as the backup of a primary drive. Equivalent to RAID 1 arrays