Population vs Sample
Populations
refers to individuals who belong to a group being studied
Sample
set of individuals taken from the population to be studied
When a population has been identified, you will need to decide on how you will obtain your data for a study. you need an appropriate sampling technique depending on the population size to come up with sampling frame that best represents the entire population
Types of Sampling
Simple Random Sampling
chosen from entire population using random number generator. each item has the same probability of being picked. everybody has a chance of being selected.
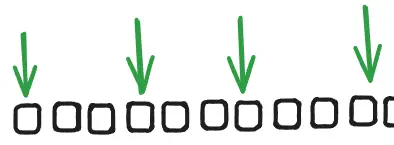
Systematic Random Sampling
random starting point is chosen, then you go through population sequentially. items are selected at regular intervals. eg. every 5th person is selected.
Stratified Random Sampling
Characteristic sampling. divide into groups that share the same characteristic. the size of each group is proportional to the size of each group.
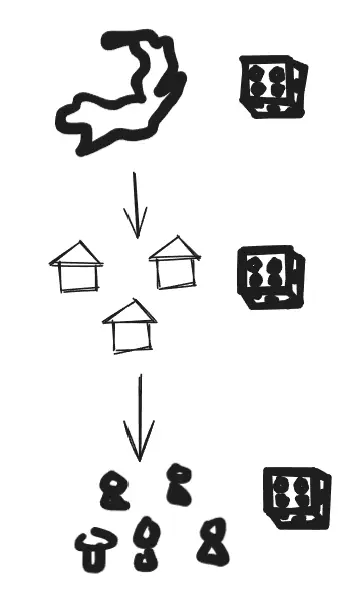
Cluster Random Sampling
If certain groups are indicative of larger populations, you use cluster sampling. You don’t necessarily choose all the groups. you choose the few groups that best represent the population. eg, sample 25 schools instead of
Multi-stage Random Sampling
the population is organized into groups. a random sample is chosen from each group a random sample is chosen. the method uses several levels of random sampling
Destructive Sampling
A random sample is taken. Each sample is destroyed during the process of testing. eg. testing the life of a lightbulb

Voluntary Sampling
The researcher invites members of a population to participate in the survey on a voluntary basis

Convenience Sampling
The researcher selects members of the population that are easily accessible. not always the best results.
Examples
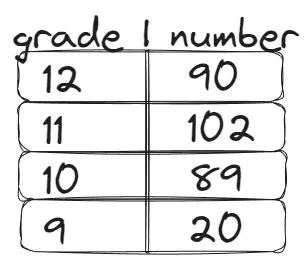
Picking 25% of the school’s music taste if there are 300 grade 9, 275 grade 10, 225 grade 11, 200 grade 12. What we use is stratified random sampling. pick generally fair percentages of each grade level, make sure the total equals to the 25% of total student population.