One of the protocols used to for data transfer on serial lines. Similar to HDLC but designed for IP. Largely replaced by IPsec
Revisions
Fields
https://www.ccnahub.com/ip-fundamentals/understanding-data-link-layer-encapsulation/ PPP has several functions useful for connecting 2 routers successfully.
- Definition of a Header and Trailer: that allows delivery of a Data frame over the Link. (Similar to other Data-Link Protocols such Ethernet Header and Trailer)
- Support for both Synchronous and Asynchronous link rates. (Symmetric or Asymmetric rates – good to for both: Home and Business users).
- A protocol Type field in the header: allowing multiple Layer 3 protocols to pass over the same link such IPv4 and IPv6.
- Built-in Authentication tools: Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) and Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP)
- Control protocols for each higher-layer protocol that rides over PPP: allowing easier integration and support of those protocols.
Encapsulation Frame
The frame looks as such:
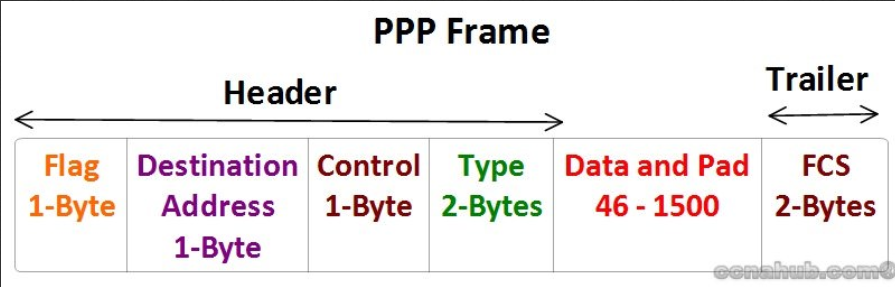 The “Type” field, similar to its use case in HDLC, tells us if this packet belongs to a IPv4or IPv6 address.
The “Type” field, similar to its use case in HDLC, tells us if this packet belongs to a IPv4or IPv6 address.