Table of Contents
Graphing Trig Functions
Sine
| x | y |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | |
| 0 | |
| -1 | |
| 0 | |
| ![[Graphing Sine Graphs-20231210194237148.webp | 265]] |
Cosine
| x | y |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 0 | |
| -1 | |
| 0 | |
| 1 | |
| ![[Graphing Cosine Graphs-20231210194335167.webp | 268]] |
Tangent
| x | y |
|---|---|
| undef | |
| 0 | |
| undef | |
| ![[Graphing Tangent Graphs-20231210195021112.webp | 177]] |
Trigonometric Function Transformation Guide
Amplitude: Half the total range of the y axis the function holds
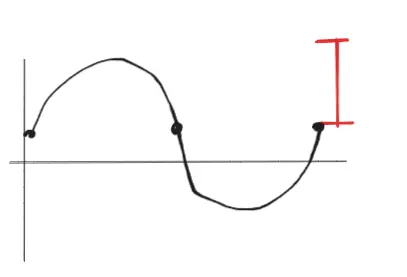 Vertical Shift: The shift from y=0 to the middle of the function
Vertical Shift: The shift from y=0 to the middle of the function
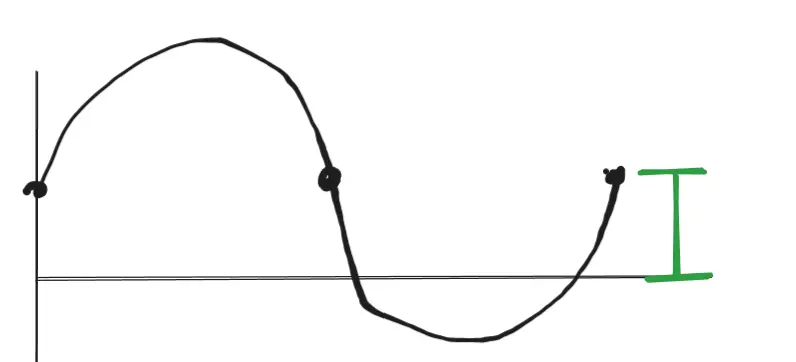 Phase Shift: The shift from x = 0 to the ‘first point’ of the function
Phase Shift: The shift from x = 0 to the ‘first point’ of the function
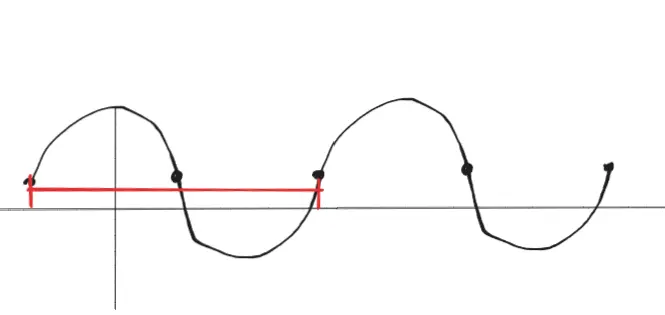
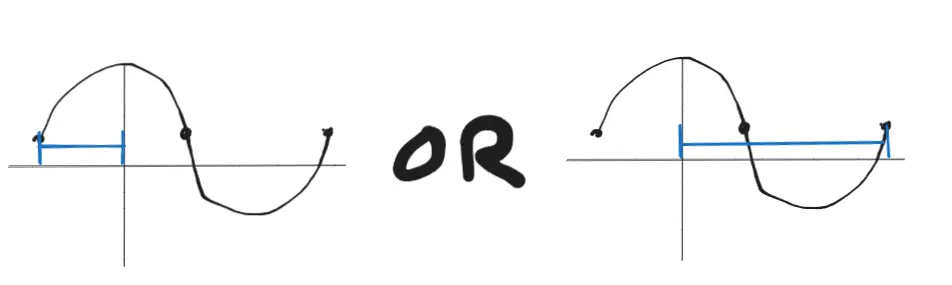 Period: The total range of a cycle of the function
Period: The total range of a cycle of the function
Formula
y = this applies to all trig functions. not just sin functions a: amplitude k: k is d is the phase shift. if d is positive, go left. if d is negative, go right c is the vertical shift. if c is positive, go up. if c is negative, go down.
Mapping rule
Y Transform
depends on a and c
stretch with a factor of a
vertical shift at c
(x, ay + c)
X Transform
period stretch of 1/k
phase shift of -d
(x/k-d,y)
Cos to SIn & Sin to Cos
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
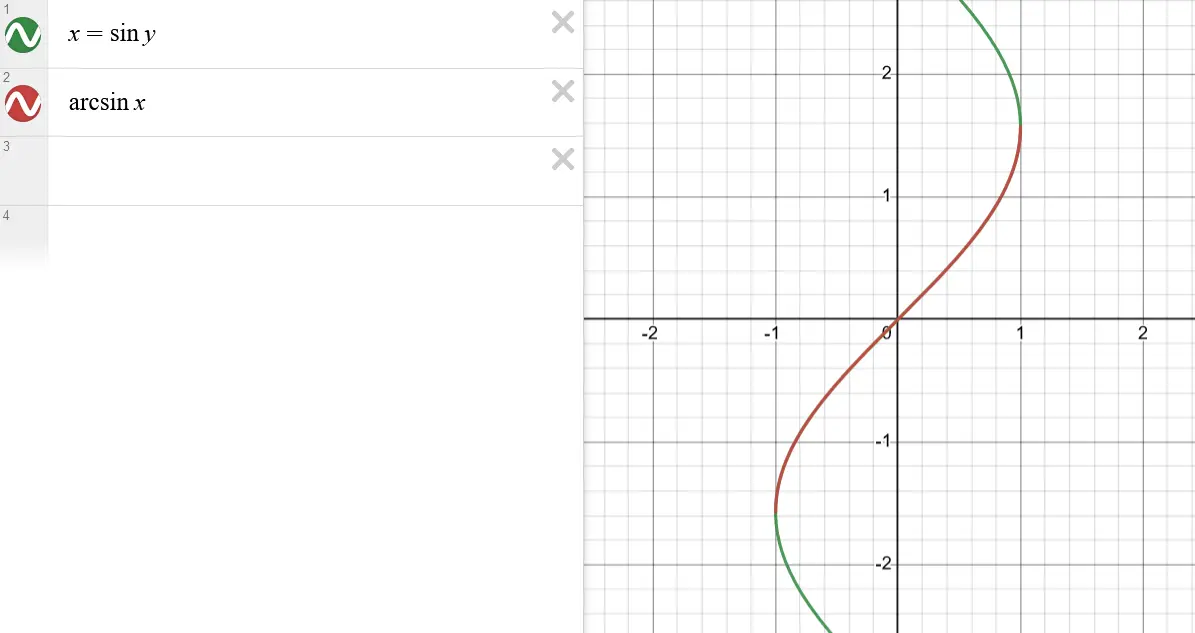
Arcsin
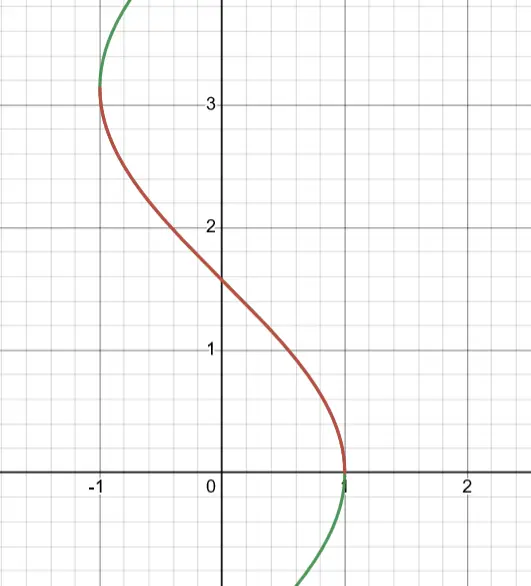
Arccos
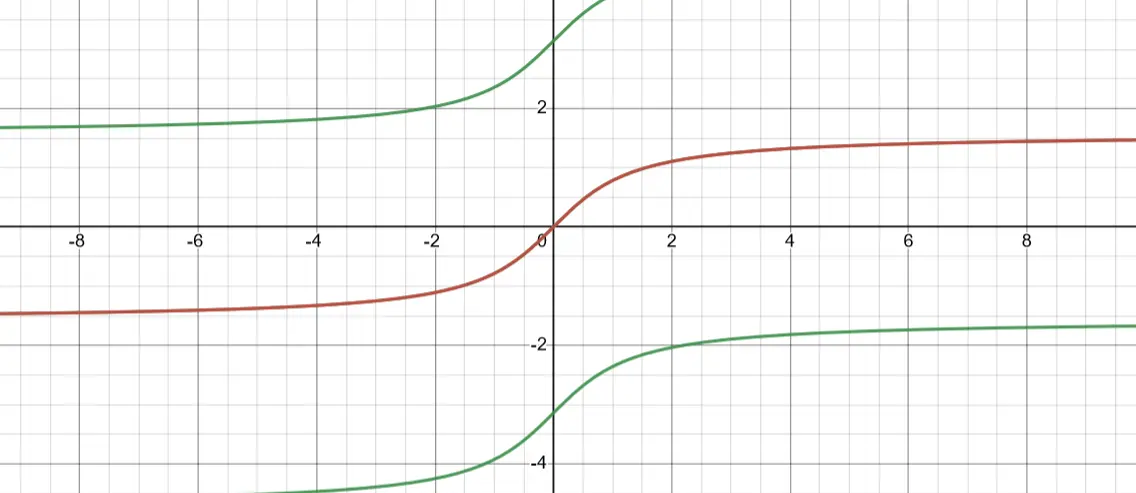
Arctan
Reciprocal Trigonometric Functions
Graph From Table Of Values
First, write the table for the original function, then find the reciprocals of all the values.
Sine → Cosecant function
| x or y | 0 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y=sinx | 0 | 1/2 | 1 | 1/2 | 0 | -1/2 | -1 | -1/2 | 0 | ||||
| y=cscx | undef | 2 | 1 | 2 | undef | -2 | -1 | -2 | undef |
notice how the table is intervals with unit circle, but there is no xpi/4 ratios
Cosine → Secant function
| x or y | 0 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y=cosx | 1 | 1/2 | 0 | -1/2 | -1 | -1/2 | 0 | 1/2 | 1 | ||||||
| y=secx | 1 | 2 | undef | -2 | -1 | -2 | undef | 2 | 1 |
Tangent → Cotangent function
| x or y | 0 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y = tanx | 0 | 1 | undef | -1 | 0 | 1 | undef | -1 | 0 | |||||
| y = cotx | undef | 1 | 0 | -1 | undef | 1 | 0 | -1 | undef |
Memorizing Reciprocal Trig Functions
Cosecant
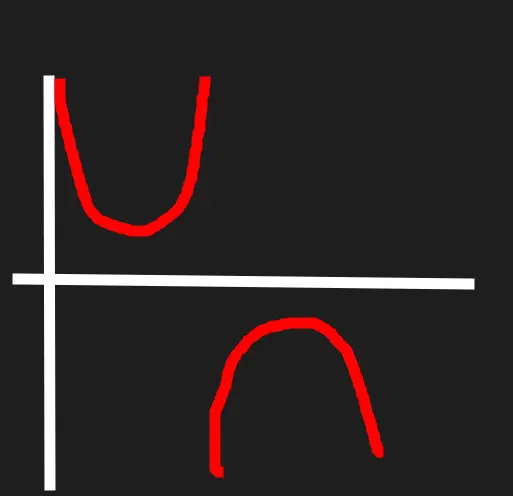 They opposites.
Local minimas are 1. Local maximas are -1
They opposites.
Local minimas are 1. Local maximas are -1
Secant
Sad face.
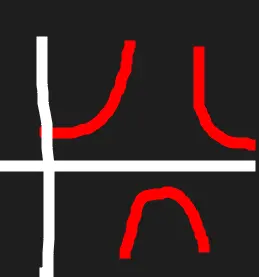 Local minmas are 1. Local maximas are -1
Local minmas are 1. Local maximas are -1
Cotangent
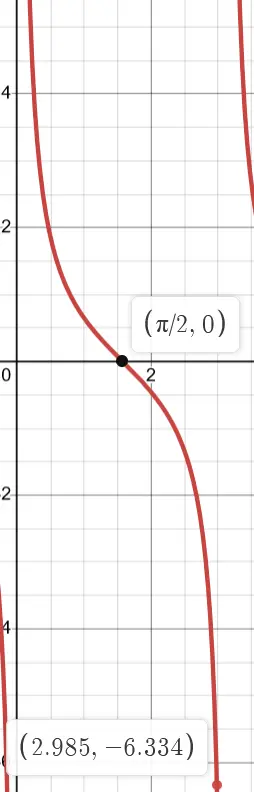 Like a flipped tangent graph that starts at 0 and ends at 2pi.
Like a flipped tangent graph that starts at 0 and ends at 2pi.