Even though, the normal is continuous, the binomial is discrete, the two are very similar. We can use the normal distribution to approximate the binomial distribution
What conditions allow us to use the normal for binomial?
- Mean = np > 5
- nq > 5
variance = npq. but np > 5
Pretty much, the distribution is not skewed.
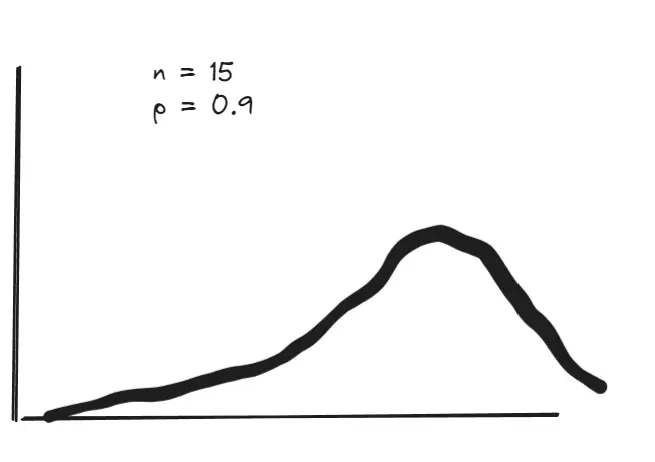 ^ Example of a distribution skewed left
^ Example of a distribution skewed left
Since, the distribution its based off is discrete, there are a few points in the continuous probability distribution that will round up to be the same. those points, we must use.
New z-scores
Area from given Interval.
Now that we have the interval, lets say 4.5 < x < 5.5, we find the probability like how we would Normal Distribution with z-score area. so, P(x<5.5) - P(x<4.5)
2<x<3 2.5 = x