Describes how an algorithm performs as its input size grows infinitely large with a chosen unit of measurement.
- Denoted as with being the smallest growing function such that
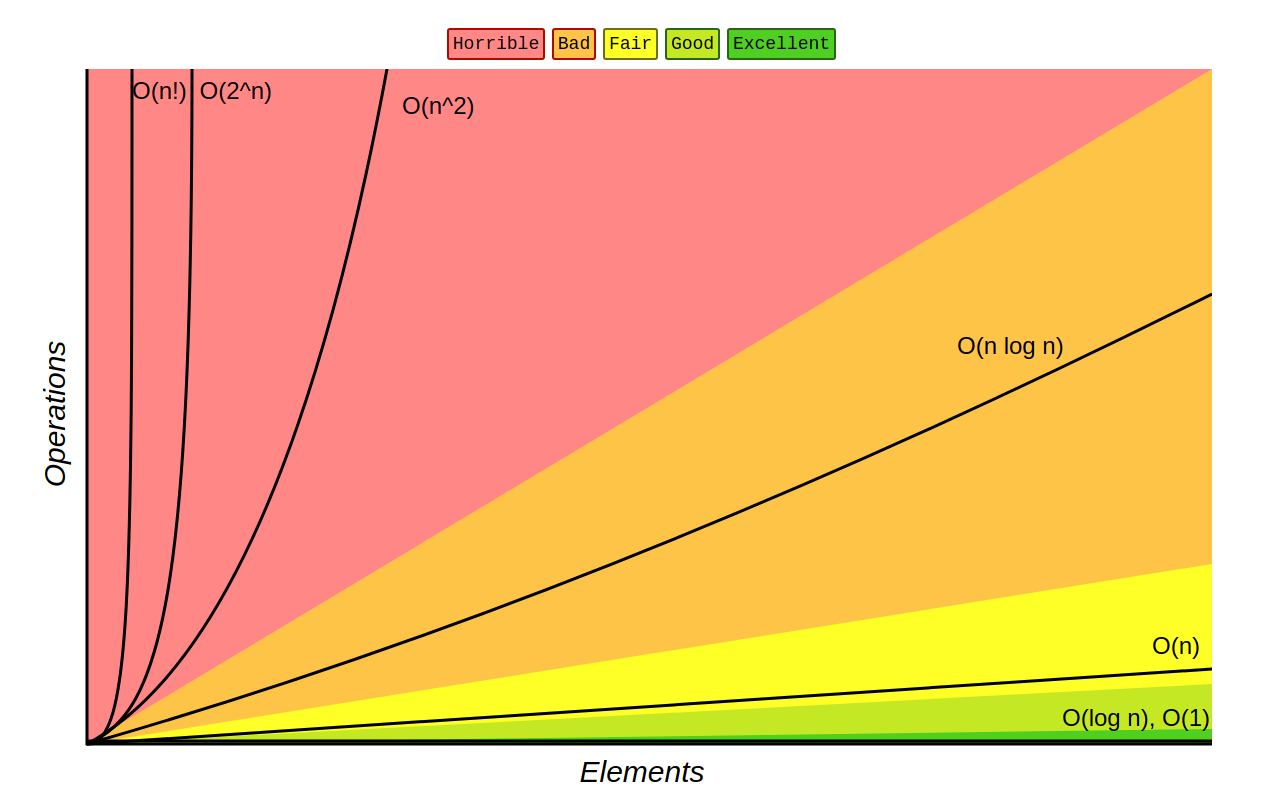
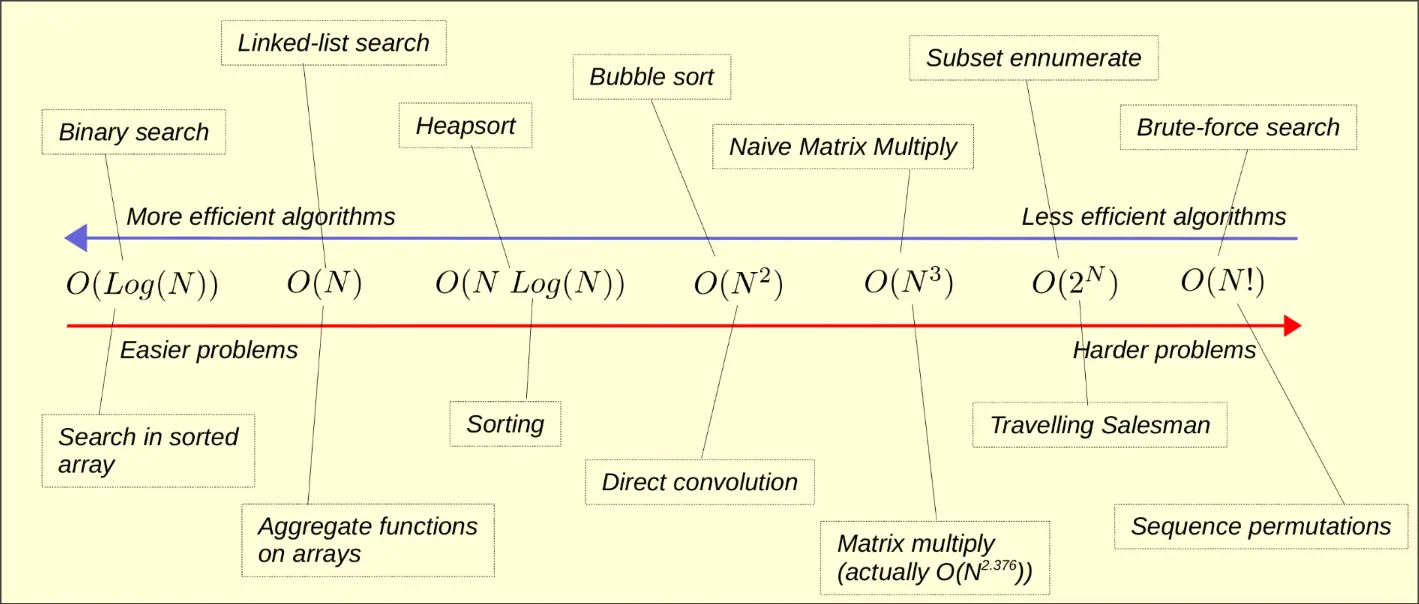
Complexity Notation
is the family of all functions such that:
- Or in other words, is always an upper bound of as
Big O Notation Simplification
Remove all coefficients and constants.
- O(2n) → O(n)
- O(2+log(n)/2) → O(log n)
- O(4) → O(1)