Table Of Contents
Elastic
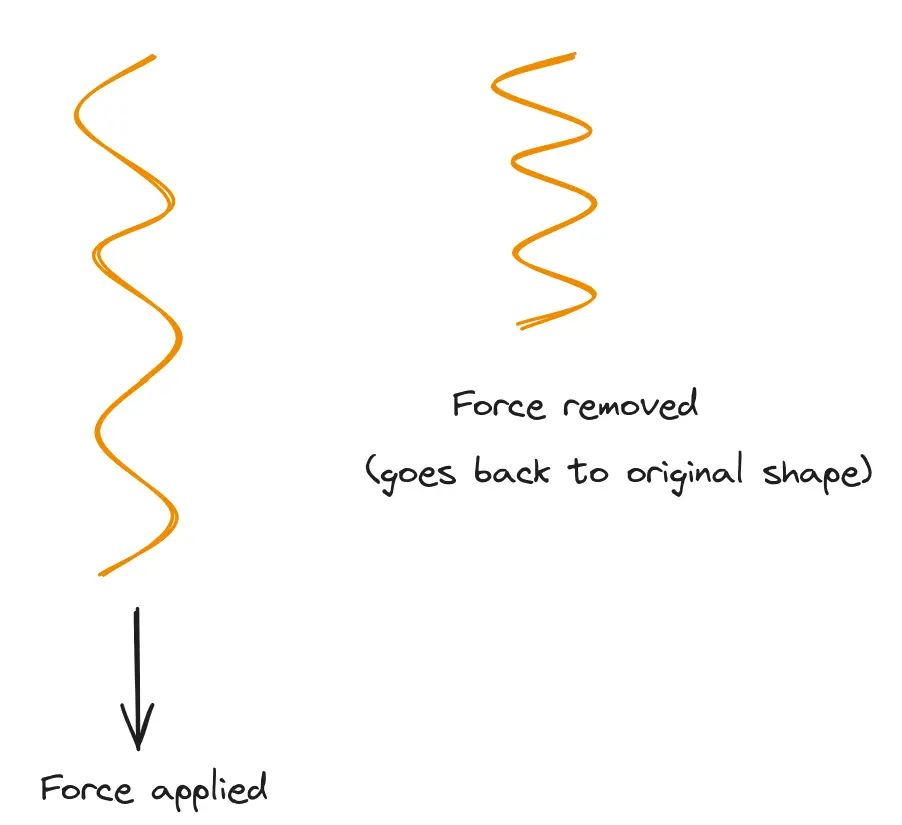 A special material that is able to return to its original shape when the influencing force is removed
A special material that is able to return to its original shape when the influencing force is removed
Properties of Elastic Systems
Damping
A higher damping more energy is lost quicker. If damping is 0, no energy is lost ever.
Spring constant (k)
This is the stiffness of the spring. It is very tricky to calculate the spring constant. Even the tiniest imperfection will change ‘k’. Springs are not designed with a specific ‘k’ in mind because it is virtually impossible to manufacture your exact ‘k’ spring.
SI Units
The SI unit for the spring constant is
Elasticity
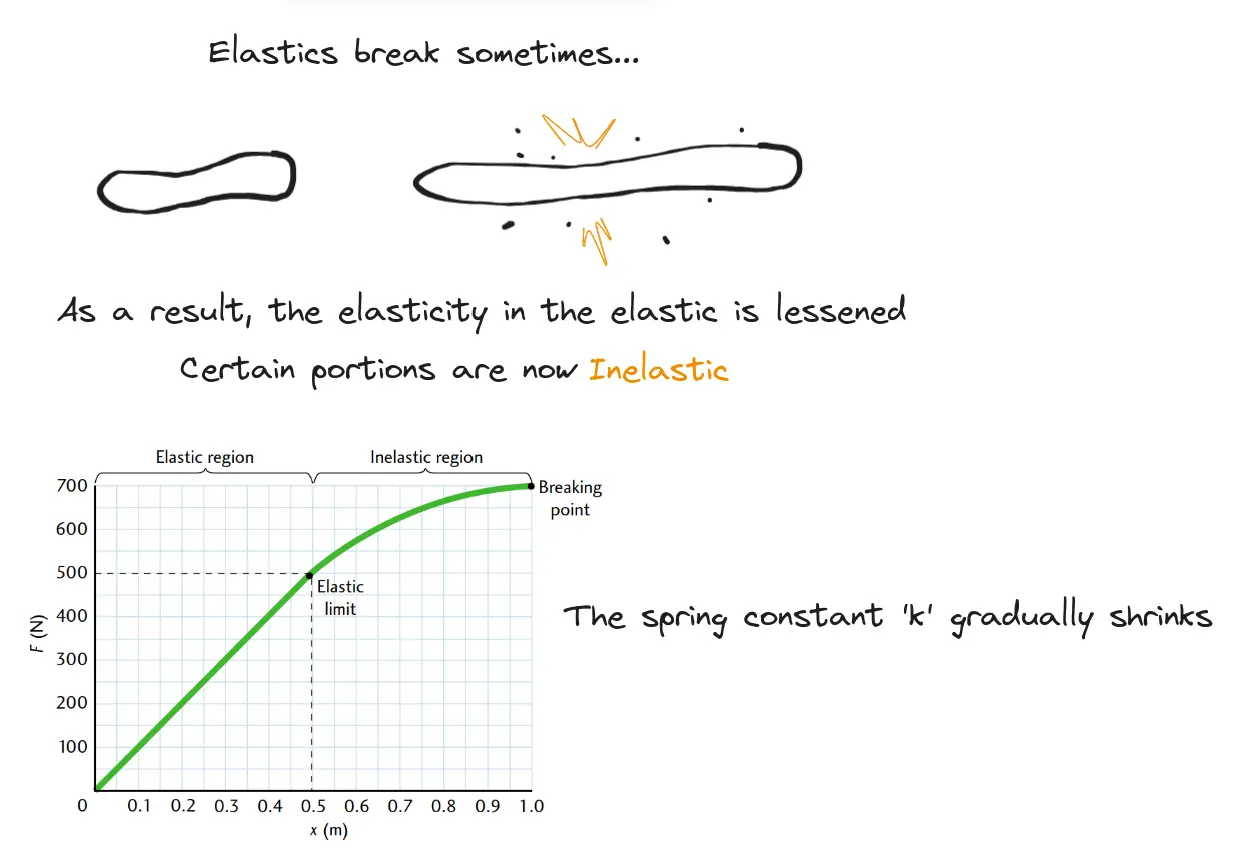
Perfect Elastic

Deformation And Energy
When an elastic is it stores energy and can release it when no force is applied.
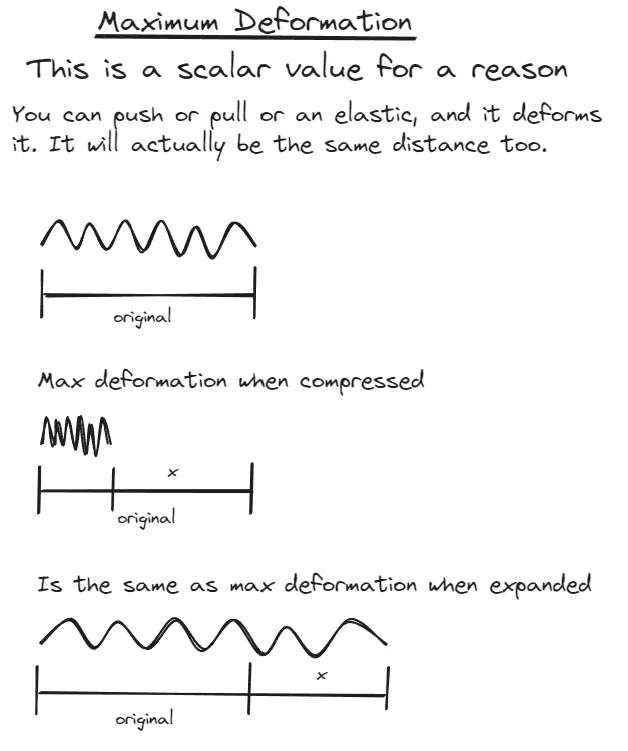
Maximum deformation is the same regardless of if you compress or expand the elastic
Hooke’s Law
Elastic Potential Energy
k : the spring constant x : length of the deformation
Elastic Potential Energy Proof
Why Strings Bounce
- Force of gravity higher than elastic force.
- Eventually it reaches an equilibrium force
- It slows down
- The force upwards makes it go upwards
- Eventually it bounces too high
- Gravity pulls it back down And the cycle repeats. Its a back and forth of elastic and gravitational energy
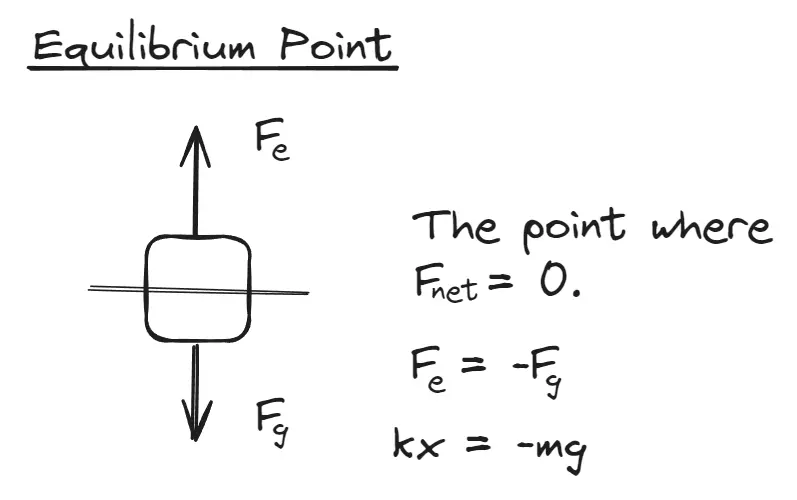
Equilibrium Point
Elasticity Coefficient (From Gizmo Lab)
If elasticity = 0, then 2 colliding objects have the same final velocity If elasticity < 1, then some energy is lost due to heat or sound. If elasticity = 1, then no energy is lost