The exam will have Stuff from test 1-3 + mean + SD Chapter 4-8
25 multiple - permutations, combinations, counting subsets, probabilities - probability (independant, mutually exclusive) - counting - permutations - combinations - counting subsets. one where you can have an empty subset, one where you cant have an empty subset. minus one if you have an empty subset - terminology. - independant or dependant - mututally exclusive or non-mutually exclusive - multiply or add - how to get dependant event probabilities - z-scores - standard deviation - mean, median and mode
5 extended response- counting, permutations, combinations, probability 1. expected value for a hypergeometric distribution 2. uniform continuous probability distribution. the one that’s the rectangle 3. normal distribution question. pay close attention to the variable 4. binomial distribution. know how to get n,p,q values 5. confidence intervals
all formulas are provided on the exam. z-score tables too.
NONE:
- NO BINOMIAL ERROR CORRECTION
- NO ONE VARIABLE OR 2 VARIABLE STATISTICS
- NO GEOMETRIC DISTRIBUTION
- NO PERCENTILES
Problem Solving
Used from chapter 4-7:
Combinatorics(Chapter 4)
- Counting
- Types of counting are:
- Fundamental Counting Principle
- Rule of Sum
- Cases
Combinations & Binomial Theorem(Chapter 5)
Probability(Chapter 6)
Probability Distributions(Chapter 7)
Normal Distributions(Chapter 8)
Terminology:
Random Variable: A discrete or continuous variable
Discrete: Integers or values that are logically finite
Continuous: Decimals or values that you MUST approximate
Bernoulli Trial: Trials where the outcome is win or lose. binary states
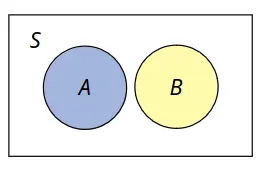
Mutually Exclusive: Sets do not overlap
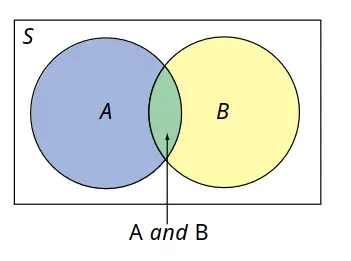
 Non-Mutually Exclusive: Sets overlap
Non-Mutually Exclusive: Sets overlap
Probability Distributions
Uniform:
- P(X) = p
- E(X) = just the mean Binomial:
- P(X) =
- E(X) = np Geometric:
- Use it to find:
- Time for something to show up
- Probability of showing up at specific time
- P(X) = q^x * p
- E(X) = q/p Hyper geometric:
- Use it when you have dependent variables
- P(X) = current case / all possible cases
- P(X) =